How To Calculate A Residual In Statistics
Hey there! So, you've probably heard the word "residual" floating around in stats class, right? It sounds a bit… mysterious, maybe even a little intimidating. Like it’s some fancy secret only mathematicians know. But honestly, it’s not that complicated. Think of it like this: we’re trying to predict something, and the residual is just the little bit we missed. You know, the leftover bit that our prediction didn't quite nail.
Imagine you're trying to guess your friend Sarah’s pizza topping preference. You know she loves pepperoni. So, you predict she'll order a pepperoni pizza. Easy peasy, right? But what if, on a whim, she orders a pineapple and ham? You were so sure about the pepperoni! That little “aha!” moment when you realize your guess was off, that’s kind of like a residual. It’s the difference between what you expected and what actually happened.
In statistics, we do a lot of predicting. We build these awesome mathematical models, these little prediction machines. They take in some information, like, say, how much someone studies, and they try to predict their exam score. Super useful stuff, no doubt. But here’s the kicker: no model is perfect. Never ever. There’s always a little bit of fuzziness, a little bit of wiggle room.

And that's where our dear friend, the residual, pops in to say hello. It’s basically the error in our prediction. The part of the actual outcome that our model couldn't explain. Think of it as the "oops, we were a bit off" sign. But don't worry, it's not a bad thing! In fact, residuals are super important. They tell us how well our model is doing. Are we consistently overpredicting? Or underpredicting? Or is our error all over the place?
So, How Do We Actually Calculate This Thing?
Alright, enough with the analogies. Let's get down to the nitty-gritty. Calculating a residual is actually pretty straightforward. It's like baking a cake: you have your ingredients (your data and model) and you have your final product (the actual outcome). The residual is like the tiny bit of batter that sticks to the side of the bowl after you've poured it into the pan. You know, that little bit you scrape out for good measure?
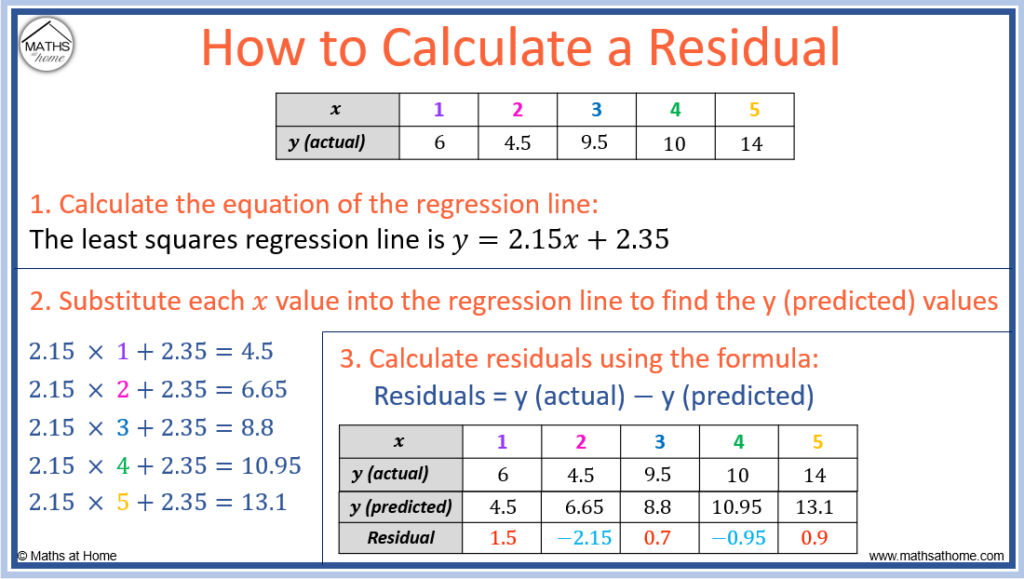
The formula is so simple, you might laugh. It’s literally just: Actual Value - Predicted Value. That’s it. Boom. Mic drop.
Let's break that down a smidge.
What's an "Actual Value"?
This is the real deal. The actual, observed data point. In our pizza example, if Sarah actually ordered a pineapple and ham pizza, the actual value for her pizza order is "pineapple and ham". If we're talking about exam scores, and someone actually got an 85, then 85 is the actual value.
It's what really happened. It's the ground truth. No guessing involved here. This is the stuff you collected, the numbers you painstakingly typed into your spreadsheet, or the observations you meticulously recorded.
And What's a "Predicted Value"?
Now, this is where our statistical model comes into play. The predicted value is what our model thought would happen. Based on all the data we fed it, this is its best guess.
So, if we built a model to predict exam scores based on hours studied, and someone studied for 5 hours, our model might predict they'd get an 80. That 80? That's the predicted value for someone who studied 5 hours.
It's the output of our fancy equations. The thing our model churned out with all its statistical might. It's like our best effort to get close to reality.
Let's See It in Action! (No, Seriously!)
Okay, okay, I know you’re itching for an example. Let’s do this. We’ll keep it super simple, because that’s how we roll.
Imagine we have a tiny dataset about how many hours students studied and their exam scores.
- Student A: Studied 2 hours, scored 60.
- Student B: Studied 4 hours, scored 75.
- Student C: Studied 6 hours, scored 85.
Now, let’s say we use this data to build a super-duper, world-class linear regression model. (Don't worry about the jargon; just think of it as a straight line trying to fit our data points). After a bit of magic and mathematical wizardry (or just using some software, let's be honest), our model might come up with a rule like: Score = 10 * Hours Studied + 40.
So, if a student studies for 2 hours, our model predicts a score of (10 * 2) + 40 = 60.
If they study for 4 hours, our model predicts a score of (10 * 4) + 40 = 80.
If they study for 6 hours, our model predicts a score of (10 * 6) + 40 = 100.
See what’s happening? Our model is spitting out predicted scores for different study hours. Now, let’s calculate the residuals for each of our students!
Calculating Residuals for Our Brave Students
For Student A:
- Actual Score: 60
- Predicted Score: 60
- Residual = Actual Score - Predicted Score = 60 - 60 = 0
Woohoo! For Student A, our model was perfect. The residual is zero. They studied exactly the amount our model predicted would get them that score. What are the odds, right? Maybe they just got lucky, or maybe our model is eerily accurate for this particular data point!
For Student B:
- Actual Score: 75
- Predicted Score: 80
- Residual = Actual Score - Predicted Score = 75 - 80 = -5
Ooh, a negative residual! What does that mean? It means our model overpredicted Student B's score. It thought they’d get an 80, but they only got a 75. So, our model was a bit too optimistic for them. It missed the mark by 5 points, in the negative direction, so to speak.
For Student C:
- Actual Score: 85
- Predicted Score: 100
- Residual = Actual Score - Predicted Score = 85 - 100 = -15
Another negative residual! Student C’s actual score was 85, but our model predicted 100. Again, our model was way off the mark here, overpredicting by a whopping 15 points. Ouch. Maybe Student C had a bad day, or maybe our model isn't quite capturing all the nuances of exam-taking for higher scores.
Why Do We Even Bother With Residuals? They Sound Like Trouble!
I know, I know. It can feel a bit like poking at our mistakes. But trust me, residuals are your best friends in the world of statistics. They're like the little detectives that help us understand if our model is actually any good.
Here’s why they’re so darn important:
1. Assessing Model Fit: Is Our Model Any Good?
The most crucial job of residuals is to tell us how well our model fits the data. If all our residuals are super close to zero, that's fantastic! It means our model is doing a pretty good job of capturing the patterns in the data. But if our residuals are all over the place, some super high, some super low, it’s a red flag. It’s like our model is saying, "I have no clue what's going on!"
We often look at the sum of squared residuals. Sounds scary, but it just means we square each residual (to make them all positive, because a big negative error is just as bad as a big positive error) and then add them up. A smaller sum of squared residuals generally means a better-fitting model. It's our way of quantifying "how wrong" our model is, and we want that "wrongness" to be as small as possible.
2. Identifying Patterns (Or Lack Thereof!)
This is where things get really interesting. By plotting our residuals, we can see if there are any patterns that our model missed. For example, if we plot the residuals against the predicted values, and we see a U-shape, or a cone shape, that’s a sign that our linear model might not be the best choice. Maybe the relationship between our variables isn't linear. Maybe it's curved!
If we see no pattern in the residual plot, that's usually a good sign! It means our model is doing a decent job of explaining the variability in the data, and the remaining errors are pretty much random noise. Random noise is good! It means we've captured the systematic part of the relationship.
3. Detecting Outliers and Influential Points
Sometimes, a single data point can be really far away from the others. This is an outlier. When we calculate the residual for an outlier, it will likely be huge. This can tell us that this particular data point is unusual and might need further investigation. Was it a data entry error? Or is it a truly exceptional case?
Residuals can also help us spot influential points. These are points that, if removed, would significantly change our model. They’re the data points that are pulling our model in a certain direction. Analyzing their residuals can give us clues about their influence.
4. Understanding the Uncertainty
The residuals help us understand the uncertainty around our predictions. If the residuals are small, our predictions are likely to be quite accurate. If the residuals are large, there’s a lot more uncertainty, and we should be more cautious about relying on our predictions.
This is super important for making decisions. If you're using a model to, say, predict sales, and the residuals are all over the place, you wouldn't want to base a huge business decision on that prediction alone. You'd want to be aware of that inherent uncertainty.
Don't Be Scared of Negative Residuals!
Remember Student B and Student C with their negative residuals? Don't let that scare you. A negative residual simply means your model overpredicted the actual outcome. It thought the score would be higher than it was. It’s not a judgment on the student or the data; it's just how our model performed for that specific observation.
Conversely, a positive residual means your model underpredicted. It thought the score would be lower than it was. Again, just a sign of how the model’s prediction stacked up against reality.
The Big Picture: Residuals are Your Compass
So, there you have it. Calculating a residual is as simple as subtracting your prediction from the actual value. But the interpretation of those residuals? That’s where the real magic happens. They are your compass, guiding you through the landscape of your data and the effectiveness of your models.
Think of them as the little whispers from your data, telling you where your model is strong, where it's weak, and where there might be hidden treasures of information you haven't uncovered yet. Don't shy away from them! Embrace them. They are the key to building better, more reliable, and more insightful statistical models. And that, my friend, is pretty darn cool.

Next time you’re looking at a statistical model, remember to peek at those residuals. They’ve got stories to tell! Happy calculating!